Describe the Structure and Function of Atp
ATP- ADP phosphate energy and here is an image for this chemical. Mitochondria are membrane-bound organelles present in the cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells that produces adinosine triphosphate ATP the main energy molecule used by the cell Table of Contents.
Atp What Is Adenosine Triphosphate What Is Atp Function Of Atp Structure Of Atp Youtube
F1 is situated in the mitochondrial matrix and Fo is found in the inner mitochondrial membrane.

. When energy is released ATP loses one of its phosphate groups and turns to ADP ADENOSINE DI-PHOSPHATE. Small amount of energy for cell work. Each ATP synthase can produce about 100 molecules of ATP every second.
It is soluble in water and has a high energy content which is primarily due to the presence of two phosphoanhydride bonds connected to the three phosphate groups. It is often referred to as the energy currency of the cell. The main function of ATP is to store energy within the cell and this energy is given out through hydrolysis reaction.
This process takes place in the cytoplasm and is known as. Therefore the role of ATP synthase is to. The enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate utilizing the energy of an electrochemical ion gradient.
It is an immediate energy source in the cell and is formed during three stages. What proteins compose the enzyme complex what are their distinct roles and how do they function in this process when hydrogen moves across the membrane. This energy is released through an hydrolysis reaction catalyzed by an enzyme called ATP hydrolase in which ATP is.
8 Structure of ATP synthase consists of two protein entities. Biology questions and answers. The function of ATP synthase is to produce ATP.
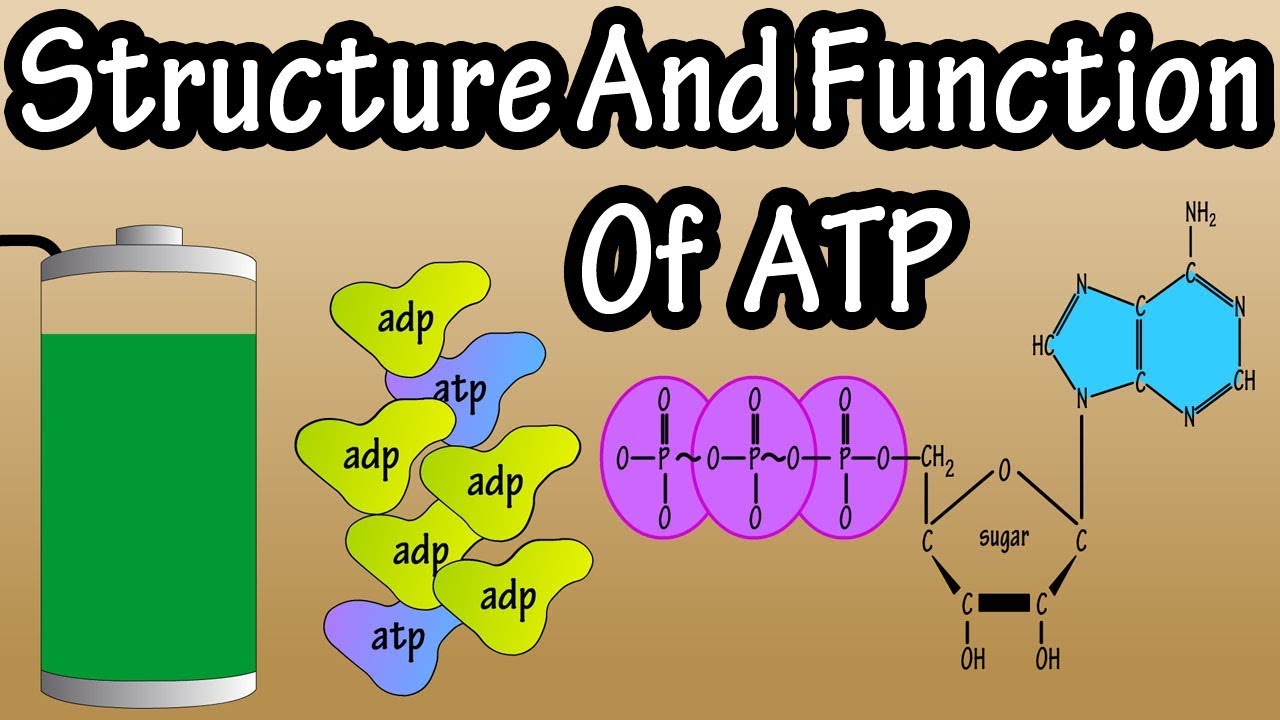
This chapter describes the structure and function of ATP synthase. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate consisting of a nitrogenous base adenine a ribose sugar and three serially bonded phosphate groups. Its main function is to store energy within the cell.
ATP Adenosine triphosphate is a nucleotide which is mainly composed of the molecule adenosine and three phosphate groups. ATP synthesis oxidative phosphorylation is critically dependent on the structural integrity of the mitochondrion. Create a table to identify the major electron carriers of aerobic cellular respiration and brie y explain how they are.
ATP consists of adenosine composed of an adenine ring and a ribose sugar and three phosphate groups triphosphate. Read on to explore what is mitochondria its structure and functions. 41 KU C 34.
ADP is present in cells and has two phosphate groups firmly attached. ATP Adenosine Tri Phosphate is a nucleotide that consists of three main structure which includes the nitrogenous base adenine. The mitochondrion less often referred to as ATP mitochondria plural is an organelle a specialized structure that performs a specific.
Structure and Function of ATP. Describe the structure and function of ATP synthase that is used to convert ADP to ATP. The energy from respiration is used to form another phosphate group to each molecule to form ATP.
ATP is synthesized through. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. ATP is an abbreviation for Adenosine TriPhosphate.
Electrons from substrate oxidations feed into the electron transport chain at complex I or complex II and then successively flow to. Explain its structure synthesis and function. ATP is a nucleoside comprised of a central ribose sugar a purine adenine base and a chain of three phosphate groups.
The sugar ribose. And a chain of three phosphate groups bound to ribose. Provides energy for cellular work.
Describe the structure and function of an ATP molecule and explain why it is so valuable to a cell. The function of ATP synthase is to synthesise ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate. ATP synthase is an enzyme located in the mitochondria and chloroplasts plant cells that produces the energy currency of the cell known as adenosine triphosphate ATP.
Eukaryotes such as plants animals and fungi have organelles called mitochondria that mainly function as ATP. Include diagrams or sketches. The enzyme complex consists of two structurally and.
ATP which stands for adenosine triphosphate is a biomolecule formed by a purine base adenine a sugar molecule ribose and three phosphate groups. It is a biomolecule consisting of a purine base adenine a sugar molecule ribose and three phosphate groups. Structure of ATP Molecule.
ATP is necessary to power all cellular processes so it is constantly being used by cells and constantly needs to be produced. On the other hand under conditions of low driving force ATP synthases function as ATPases thereby generating a transmembrane ion gradient at the expense of ATP hydrolysis. ATP is used by most all.
- motor protein - mechanical work. It is the major molecule for storing and transferring energy in cells. ATP releases energy by bonding with water a process called hydrolysis This causes one of the phosphate molecules to be released resulting in the formation of a new compound called adenosine diphosphate ADP.
The first stage begins by harvesting chemical energy from oxidation of a glucose molecule. ATP is commonly referred to as the energy currency of the cell as it provides readily releasable energy in the bond between the second and third phosphate groups. Start studying Bio Unit 40.
ATP is a very crucial molecule in body chemistry and its primary function is to serve as an energy source for the vast majority of cellular functions. This hydrolysis reaction is catalyzed by ATP hydrolase enzyme.

Adenosine Triphosphate Atp Definition Structure And Function
0 Response to "Describe the Structure and Function of Atp"
Post a Comment